Top popular Pivot Table API events

Hey there!
Missed practical tutorials?
Let’s get to know the API events of WebDataRocks better. This time we’ll cover the purposes and use cases of the most popular ones.

You might have noticed the trend of sharing with you WebDataRocks demos based on interesting datasets, mainly from Kaggle.
And there’s a strong reason for that.
Recently we’ve talked about the top frameworks in 2020. Let’s take a closer look at Vue – one of the youngest and most progressive client-side frameworks nowadays.
While React stays the most dominant of all frameworks, Vue is not far behind.
Over the last years, the community and ecosystem of Vue grew at a rapid pace. You can make sure of it by looking at the number of its uses, contributions, and stars on GitHub.
Besides, according to the recent State of JS 2019 front-end frameworks results, Vue is among top three front-end frameworks with which web developers are most satisfied.

Being a completely free-to-use project, it relies mostly on crowdfunding and sponsors. It’s supported by Standard Library, Bit, Vue School, NativeScript, Vehikl, CircleCI, and other patrons.
Features for which developers love Vue
As well as React, Vue supports the Virtual DOM, component–based approach, keeps the logic of routing and state management separated, and allows building mobile applications.
Under the hood, it unites the best features of React, Angular, and Ember and adds its own approaches.
You can use Vue’s official packages for state management, routing, server-side rendering.
Why choose Vue
The reasons to learn Vue.js in 2020 are:
- Non-steep learning curve
- Overall performance
- Elegant programming style
- Tiny size
- Well-written documentation
- A broad ecosystem of tools
- The community-driven development
Vue is considered to be a nice fit for enterprise applications. Based on feedback from software developers, you can integrate Vue into the project incrementally.
Top companies that use Vue
IBM, GitLab, Alibaba, Adobe, Xiaomi, Netflix (for internal apps), Behance, WizzAir, and Grammarly – all these companies trust Vue. They have successful examples of adopting Vue as a front-end technology.
Is it free?
Yes. As well as all great frameworks, this library is open-source and licensed under MIT.
Closing thoughts
Choosing the right framework for your web application is a real piece of work since diverse aspects should be taken into in-depth consideration. We hope this overview will encourage you to try Vue and decide whether it matches your project’s needs.
Pivot Table for Vue
Searching for a reporting tool for your Vue.js project? We’ve prepared a nicely working wrapper for you ?

The choice of a JavaScript framework always depends on project-specific requirements.
You should take into consideration various aspects: its footprint, performance, reusability, and, not of the least, community support.
Knowing how difficult it’s to always keep up with the trend, we’ve decided to make a list of the best front-end frameworks based on the personal experience and opinion of the developer’s community.
Let’s put a spotlight on these top five frameworks and libraries:
React
Whether you are a beginner or an experienced front-end developer, you would have definitely heard of React.
Created by Facebook developers with the initial intention to make their code more efficient, currently React is a leading front-end framework and the fastest growing technology. This is not surprising as it greatly simplifies the process of building rich and interactive UIs for web applications.
The results of the State of JavaScript 2018 show that during 2016-2018 years the popularity of React kept growing gradually.
What is great is that it’s backed up by the large community of developers from all around the world.
Moreover, the framework is completely user-friendly for newcomers – the guides help to cope with any difficulties that occur during the learning. Therefore, you can learn the basics of React in a few hours and master its advanced aspects with detailed documentation further.
Alongside React, developers tend to use ES6, Redux state management library, Express, Jest and React Native for a seamless mobile experience.
Developers love React for these features:
- Component-based architecture.
- An elegant style of programming and declarative views that help to produce a clear and maintainable code.
- Rapid performance due to one-way data binding which makes manipulating with the virtual DOM faster.
- Effective event handling.
- JSX – a markup syntax that keeps writing components uncomplicated.
- Adoption and popularization of a functional paradigm that eases the development and makes the management of application states more predictable.
- SEO-friendliness.
On top of that, it’s a good choice if you have to deal with real-time data in your application.
We’ve picked articles that will help you get started with React and learn more about it from a developer’s perspective:
- Thinking in React
- All the fundamental React.js concepts, jammed into this single Medium article
- React is Slow, React is Fast: Optimizing React Apps in Practice
Vue
Despite being a young framework, Vue continues to get more and more attention every month from developer’s community. It has become more stable years after the initial launch and succeeded in bringing value to a lot of startups and enterprise companies. Yes, React and Angular still win Vue in terms of overall popularity and try to put the latter in the shade, but Vue becomes gradually adopted by software developers. According to the State of JS 2018, around 50% of respondents would like to learn this framework and not without a reason.
Vue is appreciated mainly for its gentle learning curve and reduced complexity thanks to which building simple web applications takes little time. It makes the components reactive, meaning any changes applied to the state object are visible in the rendered HTML in a flash.
Good news for React and Angular developers: switching to Vue is easy as it shares concepts of both frameworks.
Other Vue’s strengths are:
- A component-oriented structure that encapsulates reusable code, gives flexibility and ensures easy scaling.
- Reactive mechanisms that help to keep the state object in full synchronization with the view and the DOM.
- Solutions for mobile UI development.
- The tiny size of the framework. It ships at only 18-21 KB.
- Helps to keep the structure of a project simple.
- Easy integration into JavaScript applications.
The last but not the least is the comprehensive documentation that covers pretty much all the features of Vue and its ecosystem. An active and ever-growing community that contributes to the development of the framework is its undeniable strength.
All in all, if you are looking for a lightweight and progressive framework which is easy to start with, Vue is a great option to try.
To dive deeper into aspects of development with Vue, we recommend reading the following articles:
- What Vue is all about?
- Understanding Vue.js Lifecycle Hooks
- Vue Development In 2019: What You Need To Know
- VueJs: The basics in 4 mins
Angular
Angular is an open-source platform for building user interfaces. It’s essential for large enterprise-scale projects and holds the top positions among front-end frameworks.
Initially, it was developed by Google engineers in 2009 and was known as AngularJS.
Later, in 2016, the framework was rewritten and started to fit the requirements of modern web development. The development team keeps releasing new versions again and again. The current version is Angular 7.0. Angular is a part of the MEAN stack that covers four major software development pillars: MongoDB, Express, Angular, and Node.js
But one should take into account that Angular more suitable for building complex long-term apps rather than SPAs as it requires a steep learning curve.
In the heart of Angular is TypeScript – a language that makes the code easier to maintain as it provides with a type system and reliable type checking. As TypeScript is updated independently from browsers, you don’t need to rely on the browser and can use all new features of the language.
Alongside the framework itself, developers use such tools as RxJS for handling asynchronous data and Angular CLI for easy creating projects, debugging and deployment.
Features for which you will love Angular are:
- Component-based architecture that reminds of MVC but makes components reusable, encapsulates the code and make it more productive.
- Two-way data binding that synchronizes the model with the view and removes the need to write excessive code.
- Hierarchical dependency injection makes components reusable and easy to maintain.
- Designed with the mobile-first approach.
- Rapid performance. However, it highly depends on the quality of the code.
- The template syntax that is easy to write and read.
- Components that ensure easy unit-testing.
- Active and large community.
- Suitable for iterative development.
All in all, Angular is an awesome front-end technology for your project if you are building complex systems but not so convenient for creating fast-changing user interfaces. For the latter case, it’s better to use React and Vue which are more lightweight and have an easier learning curve. However, Angular’s steep learning curve is compensated by the reliability of the resulting software.
To get a better understanding of Angular, we recommend diving into these articles:
Comparing popularity
Google Trends gives a good idea of how the popularity of Angular, React and Vue has been changing over the last five years:

To help you choose between these three frameworks, we recommend reading the following articles:
Backbone
Backbone.js is an open-source JavaScript library initially released in 2010. It’s acknowledged remarkably lightweight as it ships at 7.5KB and depends only on two other JS libraries – Underscore.js and jQuery. It’s licensed under MIT and everyone can contribute to its development.
Although it has been really trendy right after release, its popularity started to decline with the growth of React, Vue.js, and Angular. The results of the State of JS Survey show that it’s not among the top three most popular frameworks but nevertheless, it’s appreciated by many developers as it gives a structure to web applications. Trello, Soundcloud, Airbnb, and many other companies choose to use Backbone as a front-end technology.
Why use Backbone
As an intensive use of JavaScript makes the code difficult to organize and maintain, Backbone helps to overcome this problem by keeping business logic apart from the user interface and makes applications well-structured. In other words, it maintains the backbone of your application.
Models, Views, Collections, Events, Routers, and Sync are the basic components of the framework. It abstracts the DOM into views, data into models and binds them using events. Thankfully to communication via events, the entire code becomes easy to read and maintain.
Other fundamental features are:
- Key-value bindings for models.
- Model-view-presenter (MVP) design pattern.
- Real-time synchronization with the back-end of your app.
- A RESTful JSON interface for a server-client communication.
One more advantage is that you can use a template engine of your choice with Backbone.
Though Backbone is not so actively updated these days, the bugs are fixed and the documentation is updated systematically.
All things considered, Backbone is a great choice for building both single page applications (SPAs) and complex client-side applications.
Want to learn more about Backbone? Here is a list of articles that are worth your attention:
- Getting Started with Backbone.js
- Backbone.js: A Detailed Guide for Beginners
- Top 8 Most Common Mistakes That Backbone.js Developers Make
Ember
Ever heard about Ember?
Your favorite Apple Music is built with Ember. Netflix, LinkedIn, and Microsoft and many other popular websites use Ember.
Ember.js is a free JavaScript client-side framework released in 2011.
Being designed for creating scalable SPAs, desktop, and mobile apps, it comes together with a set of tools that make up a complete development stack. With Ember’s conventions and out-of-the-box features, developers can focus more on the functionality of their apps rather than sorting out how to configure them.
Here’s the list of Ember.js strengths:
- Built on MVVM pattern.
- Compatible with Babel – a JavaScript transpiler.
- Stability without stagnation is one of the core principles of Ember. It’s backward compatible with the older versions of the framework.
- Beautiful templates which make the user interface of your application stand out. They are written with Handlebars – a comprehensible templating language.
- Declarative two-way data binding. Templates are updated immediately once the underlying model’s data is changed.
- More than 5000 of awesome plugins available in Ember’s plugin repository. You don’t need to build from scratch an add-on – simply install it. One of the most popular is Ember-simple-auth for authentication and authorization management.
- Ember-CLI is another tool for enhancing productivity. It’s a command line utility that supports CoffeeScript, LESS, Sass, Handlebars, and more.
- Rich ecosystem and vibrant community.
- Computed properties that allow declaring functions as properties. It’s a powerful approach for creating new values.
- Object system that simplifies the understanding of inheritance and mixins.
- Easy refactoring of templates into reusable components.
Ember is built with productivity in mind and proves to be one of the most flexible frameworks nowadays. Try Ember to see whether it’s suitable for your app.
Learn more about Ember:
Comparing popularity
It can be easily noticed that Ember overtakes Backbone in popularity:

Which frameworks are the fastest?
If you’re eager to know which frameworks are the best in terms of speed and performance, we recommend digging deeper into the detailed performance benchmark results.
Final words
As developers, we know how overwhelming and challenging the process of choosing the JS framework can be.
When comparing multiple frameworks, you need to figure out how steep/gentle the learning curve is, what the nucleus of its ecosystem is, what kind of performance it provides, and more.
All the above-mentioned frameworks and libraries widen opportunities in creating outstanding UI-first applications. Now it’s your turn to decide which one is perfect for your project.
You can find more tutorials & courses for all these frameworks on GitConnected.
Further reading

There are countless reasons to enjoy winter.
Christmas lights, hot cocoa, warm sweaters, presents, and more time for visiting friends and family.
But there’s one more reason to love this magical time of the year.
And it’s the WebDataRocks new release.
In anticipation of the coming winter holidays, we’re happy to present a new milestone in WebDataRocks roadmap.
And with all the new features you’ve been waiting for, we’ve launched on Product Hunt:
https://www.producthunt.com/posts/webdatarocks-pivot-table
Please support us and share your thoughts about WebDataRocks – it will help more people discover our web reporting solution.
So, eager to know what a new release brings? Let’s dive deep into its highlights!

While Thanksgiving is a perfect time to express gratitude to people you appreciate, Giving Tuesday is a great chance to celebrate kindness and humanity. It’s an initiative that began in 2012, with a purpose to promote acting more kindly and generously.
And with this international day of charitable just around the corner, we’ve prepared a thematic tutorial for you.
Let’s take a Kaggle’s dataset about the charities in the USA and turn it into something meaningful. To explore hidden trends in the data, our helping hand will be WebDataRocks – a universal tool for reporting and data analysis.
Can’t wait to see the results? Jump right to the demo. Otherwise, let’s get hands dirty with practice!
Prettify the data
No data analysis starts without data preparation. Take a look at your data first – does everything suit you? If not, let’s put it in good shape.
Firstly, we recommend converting CSV data to JSON since this format opens up more opportunities for customization of the way fields are displayed on the grid.
Next, define the first object in the JSON array that will be responsible for setting data types and captions for the fields. Using a separate object in the data source for defining the view and properties of the fields helps avoid manual renaming fields. You can learn more details about its structure in the Data types guide.
Create a report
It’s time to pick the hierarchies you want to see on the grid. With the Field List, place them into rows, columns, and measures. Next, apply filtering to display only those hierarchies that satisfy your goals. To see the most relevant records first, sort them in ascending or descending order.
Don’t worry – you can easily arrange the fields differently with the drag-and-drop feature and look at the data from another angle at any time.

Format values
When averaging values, the numbers will likely have a lot of digits after the comma. And this is where number formatting comes in handy. Simply select the measure of interest and set needed options to beautify it:

You can also add the currency symbol and arrange its position.
Highlight values
In addition to sorting, you can emphasize values that speak most. Apply conditional formatting for this:

Now it’s easy to see in which cities animal charities have the highest revenue.
Check results
Voila! The report is ready to be presented to the audience. You can save it in JSON to restore work later or export to Excel, PDF, PNG, or HTML and share it with your colleagues.
Play with code?
Interact with a ready-to-use reporting solution on CodePen.
You can experience the full flexibility of the pivot table tool due to the dynamic nature of reports. Slice and dice your data to gain new insights about the data related to activities of charitable organizations across the USA.
About WebDataRocks
WebDataRocks is available at no cost for any kind of web project.
To dive deeper into its functionality, check out the UI Guide – it covers every feature you have access through the interface.
You can also find more information on interacting with the component via API and integrating with frameworks in the API Reference and the Available Tutorials section.
If you’d like to try creating a dashboard with a pivot table, graphs, maps, and charts, we have something for you as well – a list of guides on integration with charting libraries.

In the previous blog post, we defined a technology stack and discussed why it’s important to choose the right one for web application development.
Now it’s time to discover the most prevalent technologies that are valued both by startups and large enterprises.
Let’s dive in our top of tech stacks you should draw attention to in 2020.
MEAN
Undoubtedly, the MEAN stack is the most popular full-stack solution. Being entirely JavaScript-powered, it brings numerous benefits to web developers among which is the usage of a single language throughout your stack. Another strong advantage is that all the underlying technologies are free and open-source. The community around it is vibrant and active. If any issue arises during the development, you can always rely on its support.
MEAN presents a modern approach for developing fast and robust apps. Besides, all the components of MEAN speak JSON which makes the data flow smoothly between the layers.
Using one language (JavaScript) both for client-side and server-side development improves the communication inside the team and helps to understand your product holistically.
Now let’s break down its structure and take a closer look at its components.
- MongoDB
MongoDB is a popular NoSQL database. Unlike relational databases, it stores data as JSON-like documents. Developers appreciate this database for these key advantages:
- Scalability. MongoDB offers scale-out features, automatic sharding, and replica set to maintain constant availability
- Flexibility. Since it’s schemaless, there is no need to predefine schema. Yet, it’s recommended.
- Short learning curve. The process of configuring MongoDB is easy. Besides, MongoDB query syntax is easy.
- Performance. Due to the flexibility of JSON documents, developers can work significantly faster. Besides, documents make apps fast since all the data for an object is stored in a single document.
MongoDB copes well with big data. Due to being horizontally scalable, it fits perfectly mobile and social networking sites, e-commerce product catalogs, and any apps that rely heavily on geospatial data.
- Express.js
Express.js is a back-end web app framework that supports and hosts Node.js projects. It assists in organizing your app into an MVC architecture on the server-side. The main task of Express.js is to manage the workflow between the client-side and the data model, ensuring easy transferring of data to end-users.
Being written in JavaScript, it’s cross-platform, free and open-source. Lots of features are available for web and mobile apps.
With Express, it’s easy to build a robust API. Another thing to love Express.js for is its incredibly accurate error handling.
- AngularJS / Angular
Angular is a front-end framework, developed and maintained by Google. According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey 2019, it’s in the topmost used web development frameworks.
Angular extends the syntax of HTML, runs JavaScript code in the browser and serves to make your app’s UI dynamic and interactive. It’s mostly favored by the well-tuned performance and templates that are perfect for building the front end of cloud-native apps.
- NodeJS
NodeJS is an open-source cross-platform engine for building server-side applications. It’s the true backbone of the MEAN stack. NodeJS serves as an integrated web server for the smooth deployment of MongoDB and the app itself to the cloud.
According to the results of Stack Overflow’s Developer Survey 2019, NodeJS tops the rating of the most favorable frameworks, libraries, and tools.
With NodeJS, you can breath more functionality into your app. Built on top of Google’s V8 JS engine, it’s acknowledged as one of the most efficient and lightweight server-side frameworks. It improves runtime performance and successfully handles data-intensive tasks which leads to faster app development and better scalability. NodeJS comes with the largest repository of libraries – npm.
NodeJS is often preferred for microservice architectures. Therefore, it’s appreciated by enterprises and large-scale projects.
Companies that use the MEAN stack are PayPal, LinkedIn, Netflix, and the New York Times.
MERN
In its essence, the MERN stack is the same as MEAN stack but with Angular replaced by React. As well as MEAN, it successfully covers the full development process – from front end to back end.
React
Developed and maintained by Facebook, React is one of the most popular frameworks for building interactive UIs. It’s appreciated by the reusability of components, high performance, and smooth learning curve.
MEVN
In this version of MEAN, Angular is replaced with Vue.js as a frontend framework.
Vue.js
Vue.js is rapidly gaining popularity during recent years. It embodies the best features of React and Angular. Its key advantages are a non-steep learning curve, excellent performance, neat programming style and a rich ecosystem of tools.
LAMP
The LAMP stack is an industry-standard. It’s recognized for its performance, flexibility, and open-source nature. LAMP is often chosen for improving operational efficiency and reducing IT infrastructure costs.
Let’s take a look at its structural components.
- Linux
Linux is an operating system and a first layer of the stack. All subsequent layers run on top of it.
- Apache
Apache is an open-source and free HTTP server that transfers the content between the server and client machines upon request. To be precise, it fetches the content from the server, turns it to static HTML files and returns it to the browser.
To be precise, it’s not a physical server but a software that operates on the server. It establishes a connection between a server and browsers of users (Google Chrome, Safari, Firefox, etc).
Since Apache is a cross-platform software, it works on Unix and Windows servers.
Due to its module-based structure, it can be customized to enable security, caching, password authentication, etc.
- MySQL
MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS). It stores information that can be requested to build a website.
- PHP
PHP is a programming language. Instead, you can use a similar web programming language, e.g., Perl or Python.
All these layers are open-source and free products. However, since the stack can run smoothly on any operating system, you can choose different modifications and variations of the same stack:
- WAMP (Windows OS, Apache, MySQL, PHP)
- MAMP (Mac OS, Apache, MySQL, PHP)
- WISA (Windows, IIS, SQL, ASP.NET)
- BAMP (BSD, Apache, MySQL, PHP)
- XAMPP (distribution that contains MariaDB, PHP, and Perl)
- SAMP (Solaris, Apache, MySQL, PHP)
RoR (Ruby on Rails)
Ruby on Rails is a web framework written over Ruby – a dynamic programming language with an elegant syntax. With Ruby on Rails, you can build a complete web application by combining HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and Ruby.
Ruby on Rails has a lot of supporters since it makes writing and debugging code faster and easier. The greatest thing is that Ruby developers can reap benefits from open source tools that speed up development.
Signature stacks
Now that we considered standard solution stacks, let’s discover which bundles of technologies stand behind popular web apps. The following combinations of technologies can be categorized as “signature stacks”.
Uber Tech Stack
- Web server: NGINX, Apache
- Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB
- Server-side framework: Node.js
- Programming languages: Python, Java, JavaScript, Objective-C
Reddit Tech Stack
- Server: NGINX
- Databases: PostgreSQL, Redis
- Server-side framework: Node.js
- Programming languages: JavaScript, Python
Pinterest Tech Stack
- Programming Languages: Python, Java, Go
- Framework: Django, Javascript MVC
- Databases: MySQL, Hadoop, HBase, Memcached, Redis
- Server: NGINX
Facebook Tech Stack
- Programming Languages: PHP, GraphQL, Hack
- Framework: Tornado
- Databases: Cassandra, RocksDB, Beringei, Memcached
- Server: custom/proprietary
Airbnb Tech Stack
- Programming Languages: JavaScript, Ruby
- Framework: Rails
- Databases: MySQL, Amazon RDS, Hadoop
- Server: NGINX
This time we covered the time-tested tech stacks that are used widely across modern applications. The right tech stack directly affects the success of your project. Hopefully, today you’ve got the step closer to finding your perfect match.
Empower your tech stack with analytics
If your app needs analytical and reporting features, you can always rely on WebDataRocks. Integrating with any front-end technology of your technology stack is as simple as ABC – check out available tutorials to make sure how seamless the entire process is.
We continue our blog series on discovering awesome data visualization types. This tutorial suits everyone who wants to understand their geographic data better.
Today we’ll focus on using one of the most popular visualization techniques for geospatial data – a choropleth map. And not only you’ll learn how to use this chart to represent the geodata but also how to efficiently combine it with a pivot table on a dashboard.
Here’s what you’ll get as a result:
See the Pen WebDataRocks Pivot Table with Google Charts Map by WebDataRocks (@webdatarocks) on CodePen.
But first things first: what is a choropleth map?
Choropleth map
Choropleth map is a data visualization technique that allows representing the data using different colors or shades of one color for different regions. Most often, it’s used to visualize how the variable varies across a certain geographic area. You can use this technique to communicate the correlation between the variable and a geographic location.
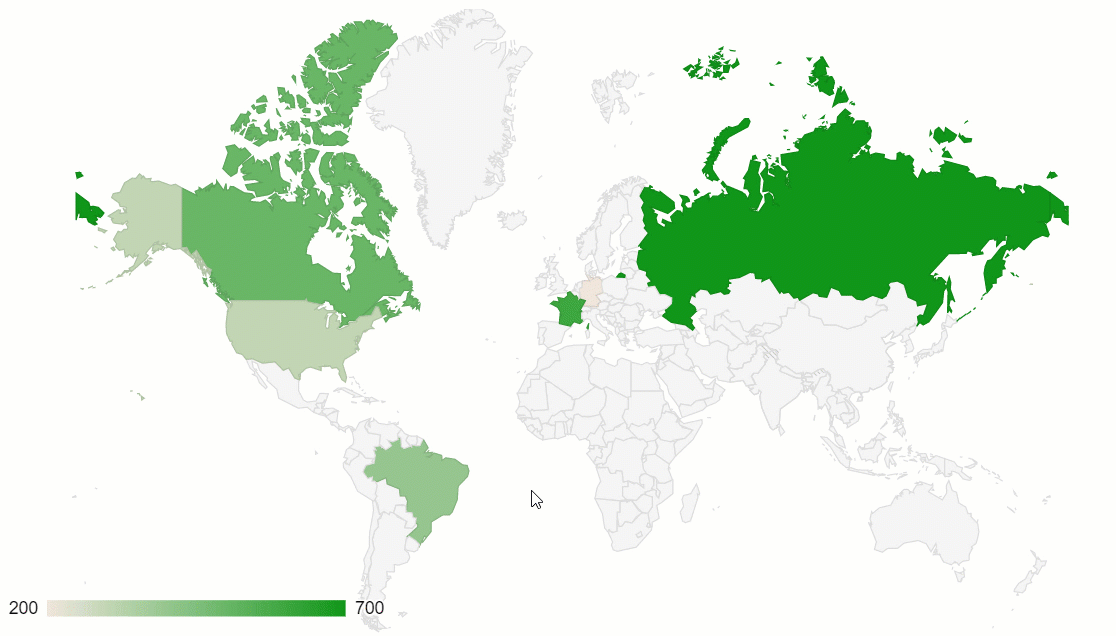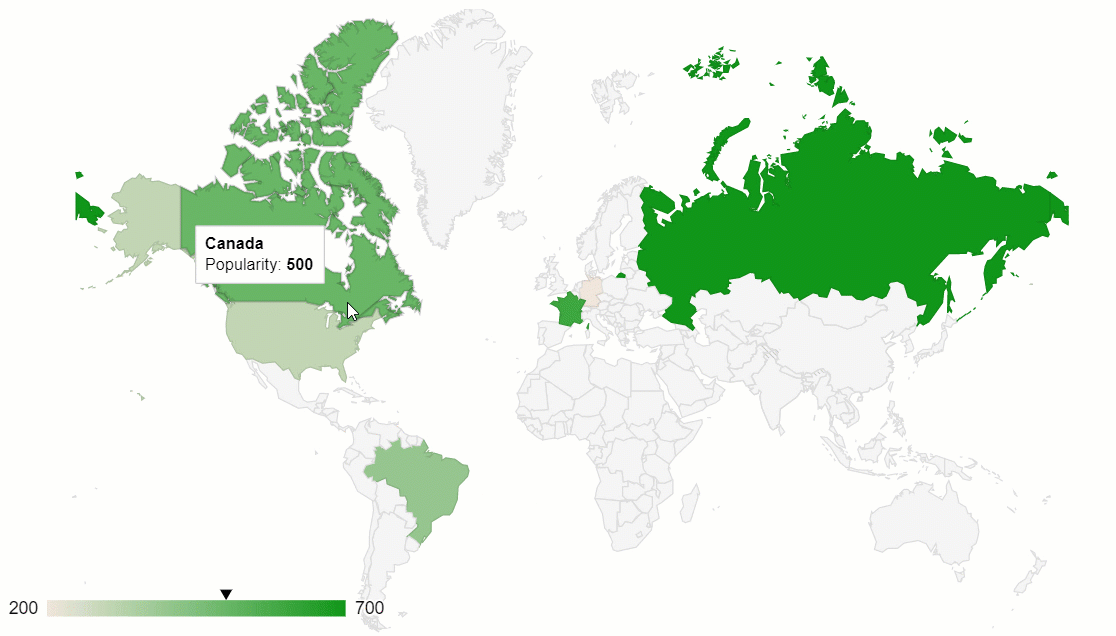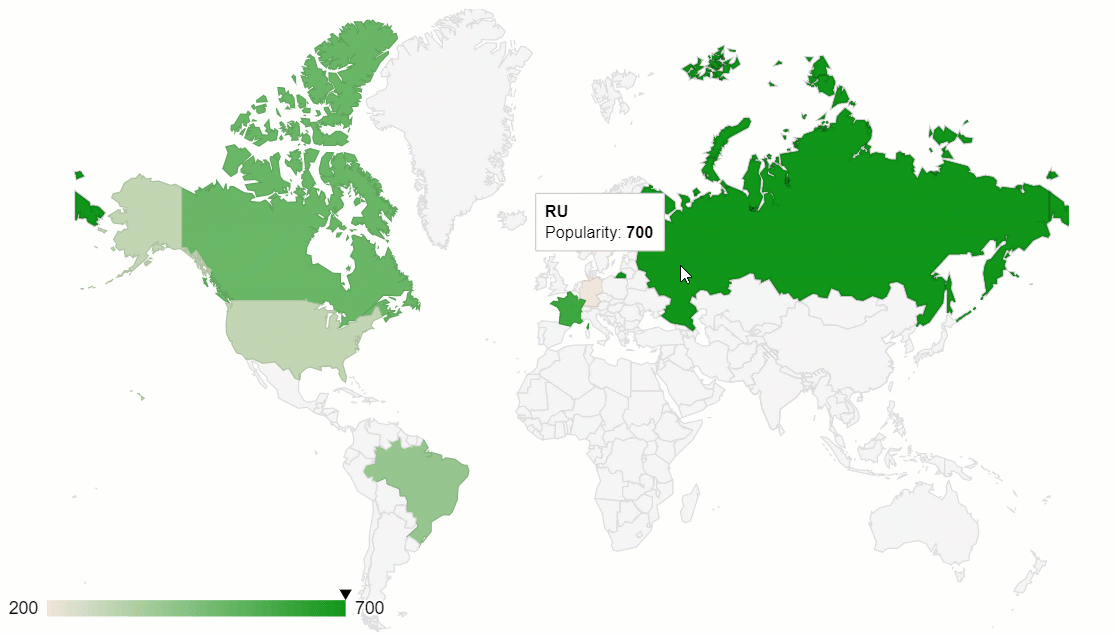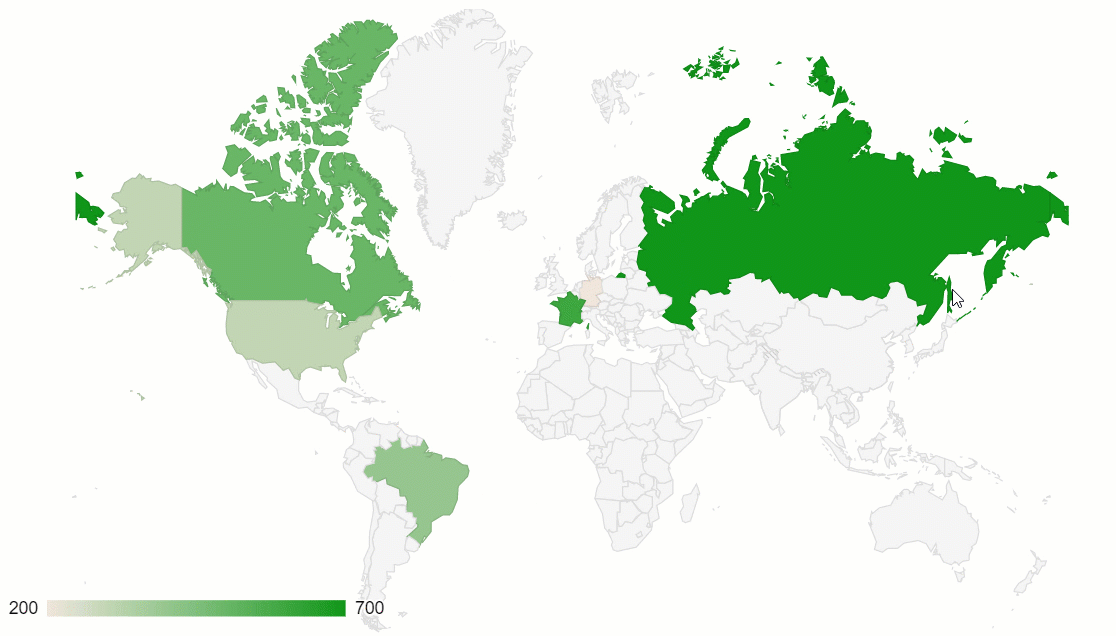
One of the best implementations of this data visualization method is a geo chart by Google Charts. Plus, it can be perfectly combined with another data visualization type – a pivot table.
Now let’s figure out how to create a dashboard in five simple steps.
Step 1: Add a web reporting tool
The first step is to include the pivot table on the page. For this, we should follow the straightforward steps from the Quickstart guide.
Step 2: Connect your data
Choose the data format you prefer and load the file into the pivot table by specifying its URL or the name of the function that returns it.
Here’s how you can specify the data source in the report object:
filename: "URL-to-your-CSV-or-JSON-file"
or
data: getData()
Step 3: Create a tabular report
Now it’s time to select the fields to be displayed on the grid. Let’s put the “Country” hierarchy to the rows, “Category” to the columns and aggregate this data by “Revenue” – a calculated value built using “Price” and “Quantity” measures:
"slice": {
"rows": [{
"uniqueName": "Country",
"sort": "asc"
}],
"columns": [{
"uniqueName": "Category",
"sort": "asc"
}, {
"uniqueName": "Measures"
}],
"measures": [{
"uniqueName": "Revenue",
"formula": "sum(\"Price\") * sum(\"Quantity\") ",
"individual": true,
"caption": "Revenue"
}]
}
Step 4: Integrate with Google Charts
Add the Google Charts loader to the <head> section of your web page:
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/charts/loader.js"></script>
To have access to the data preprocessing methods of WebDataRocks, include its connector for Google Charts:
<script src="https://cdn.webdatarocks.com/latest/webdatarocks.googlecharts.js"></script>
Create a <div> container to hold the chart:
<div id="googlechart-container"></div>
Step 5: Connect the chart to the pivot table
Now that we’ve set up the web reporting tool and charts, let’s synchronize them.
For this, we need a reportcomplete event. It’s triggered once the report has completed loading into the pivot tool.
Here’s how we can attach an event handler to it:
reportcomplete: function() {
pivot.off("reportcomplete");
}
Additionally, we need two flag variables to track when both charts loader and the report are ready to be used:
var pivotTableReportComplete = false; var googleChartsLoaded = false;
For loading the charts, we need to specify the mapsApiKey parameter:
google.charts.load('current', {
'packages': ['geochart'],
'mapsApiKey': 'AIzaSyD-9tSrke72PouQMnMX-a7eZSW0jkFMBWY'
});
We also need to set the callback function for the google.charts module to track if it’s finished loading:
google.charts.setOnLoadCallback(onGoogleChartsLoaded);
Once we’ve configured everything, let’s move on to a more creative part of the tutorial – drawing charts.
Create the functions that are responsible for handling the drawing logic:
function createGoogleChart() {
if (googleChartsLoaded) {
pivot.googlecharts.getData({
type: "bar"
},
drawChart,
drawChart
);
}
}
function onGoogleChartsLoaded() {
googleChartsLoaded = true;
if (pivotTableReportComplete) {
createGoogleChart();
}
}
function drawChart(data) {
var data = google.visualization.arrayToDataTable(_data.data);
var options = {
colorAxis: {
colors: ['#449544', '#4ca64c', '#7fbf7f', '#b2d8b2']
},
backgroundColor: '#b3e5fc',
datalessRegionColor: '#ffffff',
defaultColor: '#f5f5f5',
};
var chart = new google.visualization.GeoChart(document.getElementById('googlechart-container'));
chart.draw(data, options);
Since for mapping data, we’ll use a single-hue progression, in the colorsproperty, we should specify the palette – all the shades of the chosen color, from the lightest to the darkest. The darkest hue represents the largest values of the data, the lightest – the smallest values.
So, after we’ve defined all the needed functions, here’s how our event handler for reportcomplete looks like:
reportcomplete: function() {
pivot.off("reportcomplete");
pivotTableReportComplete = true;
createGoogleChart();
}
Results
Hooray! Now your dashboard is rendered on the web page and we can use it for deriving insights from the geographic data.
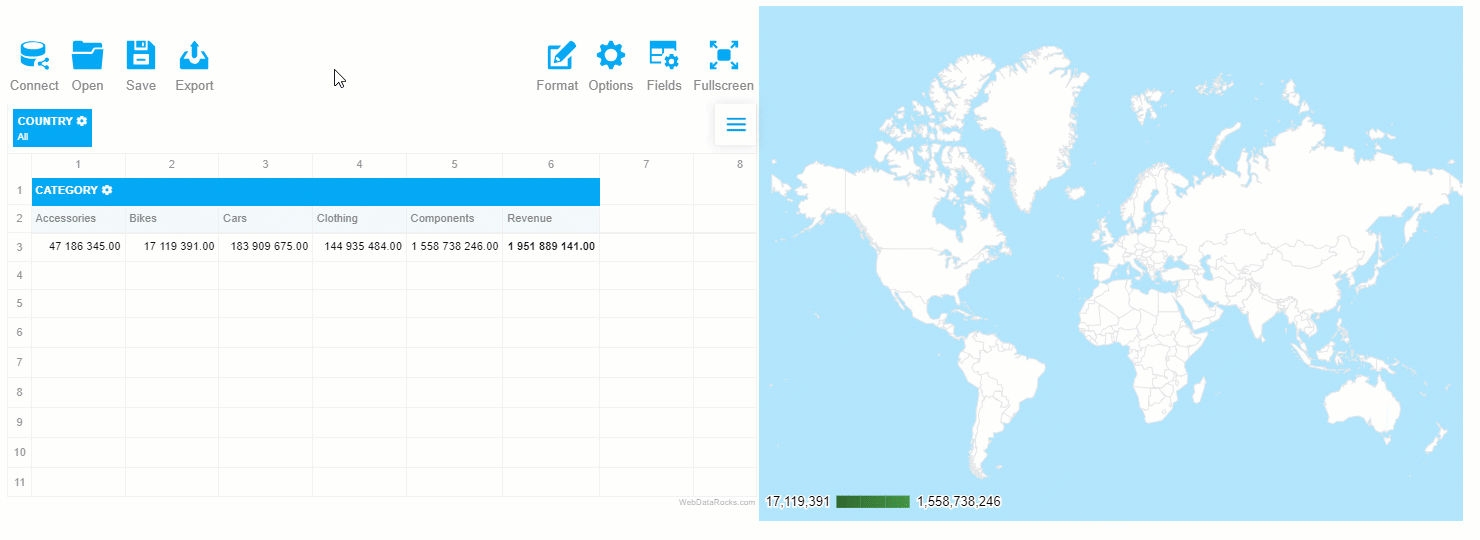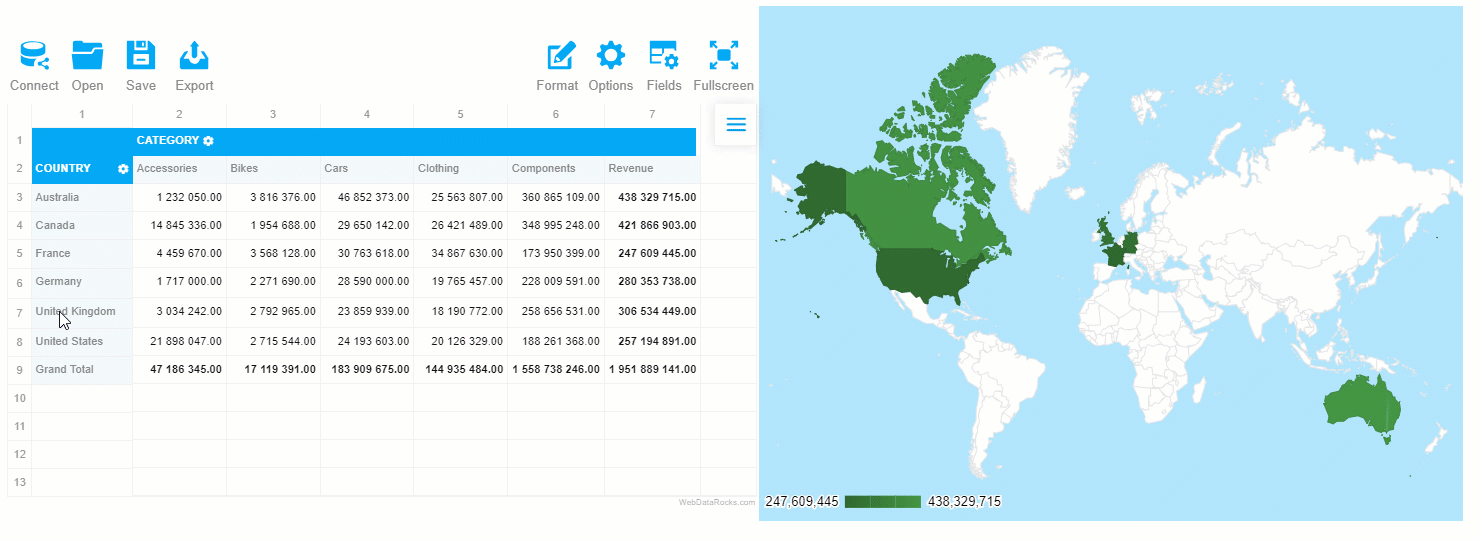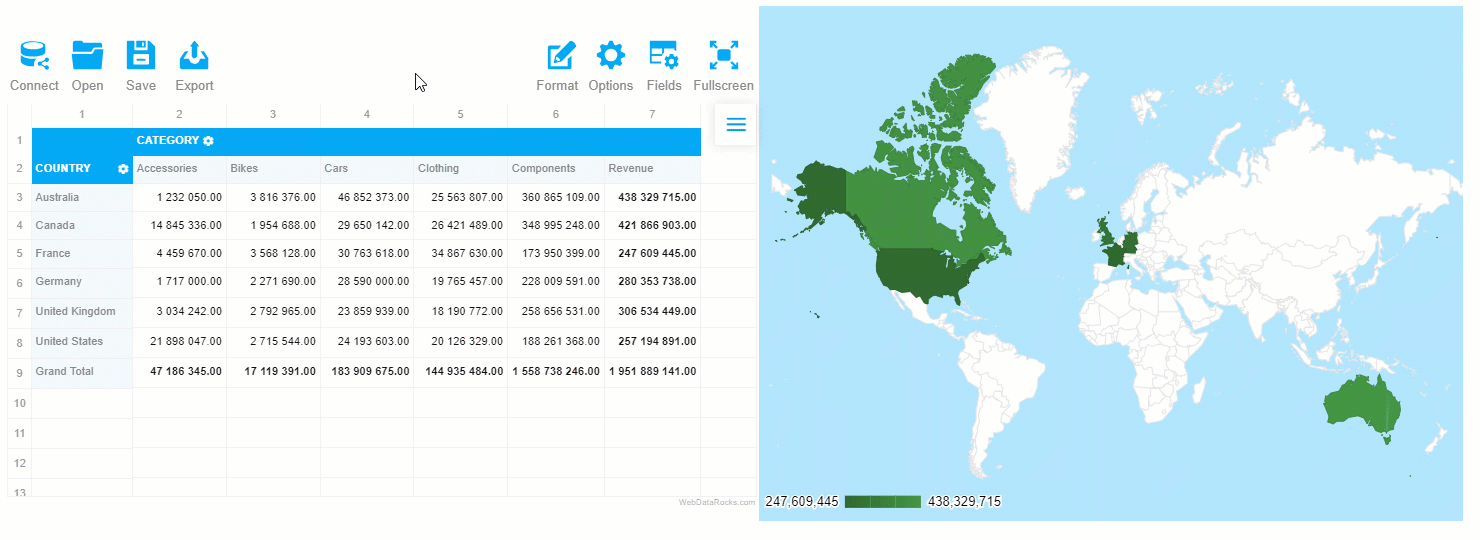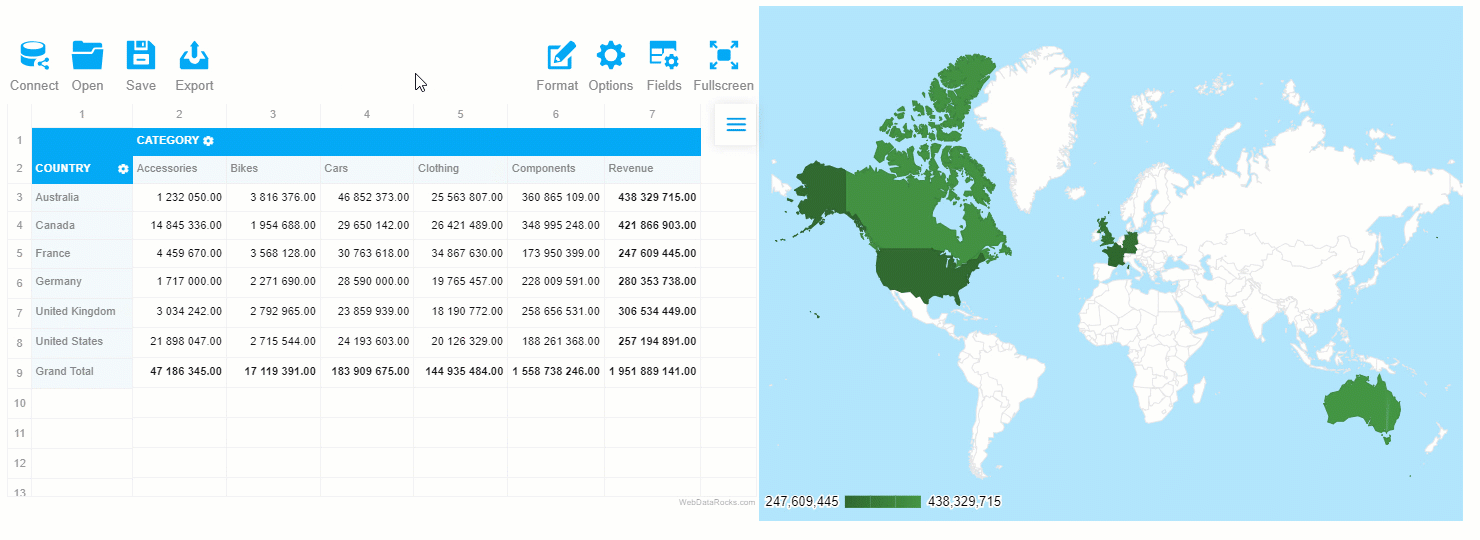
The greatest thing about such a data visualization approach is that the elements on the dashboards are connected – the chart reacts to the changes applied to the report. Try filtering the data or moving the hierarchies between rows and columns to see the synchronization in action.
What’s next?
Eager to discover more features of WebDataRocks Pivot? Check out our tutorials on integration and the UI guide.
Want to customize the charts further? The editable examples from the Google Charts documentation will help you to find out how to do it.

Let’s outline the essential aspects every developer needs to know about a technology stack and how its selection can affect the entire process of software development. Further, we’ll stress the top things you should pay attention to when choosing the tech stack for your project.
We do hope that this article will help you get a full picture of the tech stack’s purpose and understand how to make a smart choice of the one that fits your project at best.
Let’s start!
What is a tech stack in software development?
Even if you are already well-familiar with the concept, let’s recap its definition.
A tech stack (also known as a solutions stack) is a bundle of tools, namely programming languages, libraries, frameworks, and databases that come together for the development of a particular web, mobile, or hybrid application.
Such a name is given to this concept not without a reason – each subsequent layer of the stack builds on top of the features of one underneath it. All of them are brought together around one common goal – to assist in building, testing and running your application.
Though this concept can be found in many areas, the term itself emerged in the software development community. It meant to simplify communication between developers and help to indicate the application’s strong and weak points.
Structure of a tech stack
Every tech stack is different, yet, they all share a common structure. It’s comprised of two major components – front end and back end. The front end is responsible for the client-side part of your app while the back end is in charge of its server-side functionality.
What is a back end stack?
A back end is the backbone of your application. It refers to everything that is not visible to users but ensures the proper functioning of the app. Behind the scenes, it takes care of things like security, content management and the structure of your app.
Structurally, the back end consists of the following components:
- Programming languages (JavaScript, Node.js, Ruby, C#, Perl, PHP, Python, Java, Go, Scala, Elixir, etc)
- Server-side web frameworks (e.g., .NET, Django, Flask, Mojolicious, Laravel, CakePHP, Ruby on Rails, Phoenix, Express JS, AdonisJS, Spring Boot, etc)
- Databases (MySQL, Oracle, MongoDB, GraphQL, etc)
- Web servers (Nginx, Express, Apache, Apache Tomcat, IIS, Google Web Server, etc)
Let’s break down the purposes of all the back end’s building blocks. A back-end developer has to work with programming languages that databases understand to ensure the communication between web services, database systems and the application itself. A framework simplifies and speeds up development. A database is used for storing your application’s data. In addition to a database, a caching system is required to be set up to reduce the load on your database (e.g., Memcached, Redis, etc). A web server handles requests that come from the client-side, i.e., your app’s users.
What is a front end stack?
And now let’s look at the front-end more closely.
A front end is responsible for a visual part of an application. It defines what your users see and how they can interact with your app. The core purpose of front-end web development is to create a seamless user experience and maximize its quality by making the interface accessible to any user.
As a rule, a front end is a part of the project where the development starts since it’s the most important thing to show to your customers in the first stages.
What are the cornerstones of the client-side?
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
This is a classical trio of tools for implementing designs on the web. HTML defines the structure and layout of the application’s content. CSS tells the browser how this content has to be styled with colors, fonts, etc. JavaScript is a scripting language that is responsible for making web pages interactive (i.e. defining the rules of how, when and where the content should be modified, hidden or removed). Often, front-end development becomes heavily JavaScript-oriented, especially if a web application is highly interactive.
A modern front-end developer needs to be familiar with the principles of responsive design, test-driven development, front-end frameworks and libraries (React, AngularJS, Angular, Vue, Ember, Bootstrap, Foundation), and basics of server-side rendering. Also, knowledge of the principles of working with SASS and LESS adds a competitive advantage since these pre-processors for CSS provide more flexibility and modularity when it comes to your app’s styling. Front-end developers should know how to use graphic design tools that allow building the application’s prototypes, experiment with the user interface and deliver the final variant. The most popular software is Balsamiq Mockups, Illustrator, Figma, Photoshop, Sketch. Try at least several of them to find your perfect match.
Why tech stack matters
The technology stack is a foundation of your application. The underlying technologies make a significant impact on how your app is functioning and how it will perform in the future. It also can affect the scalability of your app. That’s why developers should take the task of selection responsibly and with exceptional care.
Once you’ve chosen the tech stack, try to understand its strengths and weaknesses. This will help you to know how to benefit from the former and alleviate the latter.
How to choose your tech stack
If you struggle to make the right choice on the tech stack, there are some general guidelines for you to follow.
- Take into account the size of your project – it can be small, mid-range or large. Small projects are often built on top of Node.js – React and Python-Django stacks. If you need only a simple landing page, consider using WordPress. Mid-size projects (e.g., online stores, etc) need more complex stacks such as MEAN, LAMP, or MERN that prove to perform well. Large projects require more scalability, speed, and maintainability. So, you need to find the stack that leverages well both performance and customer satisfaction.
- Scalability. Depending on the technologies you choose, your app may have different scalability capabilities. This factor should be taken into consideration as early as possible. If you are building a service that will be accessed by thousands and millions of users, think about programming languages that support high-read operations and databases that are scalable. In this case, you can try MEAN stack.
- Consider your app’s type. Will it be a mobile or desktop app? If a mobile, then for which platform – Android or iOS? If a desktop, which browser will it use? It’s always better to launch the MVP of your app only on a single platform – web or mobile. After you made enough process in developing and distributing your product, you can proceed to build the second app’s interface.
- Stick to the mobile-first design paradigm and build a responsive web application.
- Make sure you have enough engineers with the required skills.
- Try to predict whether your tech stack will scale. However, the lion’s share of performance issues is related to application design rather than a choice of technologies. So, be ready to tune and optimize your app’s design.
- Evaluate the cost of development. After studying carefully the tech stacks that correspond to the needs of your app. Before choosing the paid tools for development, compare the cost of a resulting stack and usability of the features it provides. Rather than investing in expensive tools or building custom ones from the ground up, try researching their free alternatives. You can reap a lot of benefits from the open-source products.

Vue.js is a progressive JavaScript framework that enables web developers to create UIs in an elegant and efficient manner. Lately, it started to attract more and more attention from wider circles of the web development community.
And not without a reason – among the most prominent features of Vue are a smooth learning curve, concise programming style and high performance due to the automatic tracking of the component’s dependencies during its rendering. Besides, its core concepts are well-documented.
As the Vue.js community grows in size, so does its ecosystem of development tools. Let’s explore its best representatives in more detail.
Vue CLI
Vue CLI is a standard utility for rapid Vue.JS development. It provides your Vue app with access to the build tools and ensures they work smoothly together, allowing you to fully concentrate on bringing your ideas with code rather than on configuring the app.
The flexible plugin system of Vue CLI supports Babel, TypeScript, ESLint, PostCSS, PWA, Jest, Mocha, Cypress, and Nightwatch. Plus, thanks to this system, developers can share their plugins with the community.
To my mind, the greatest thing is that you can make use of various configuration and customization options to meet your project’s specific needs.
Another thing you’ll love is a mighty GUI of Vue CLI that makes creating, configuring and managing projects a lot easier. Besides, Vue CLI has out-of-the-box support of unit & end-to-end testing.
Storybook
Storybook is an open-source environment for developing, managing and testing UI components. Seamless configuring components through a flexible API is what makes it a must-have tool for building UIs efficiently.
With Storybook, you can create awesome components and demonstrate them in an isolated environment. Since it runs outside your app, you don’t need to worry about your app’s dependencies and specific requirements.
If you want to implement extra features for Storybook, you can try addons functionality.
Vuetify
Vuetify is a component framework that offers a broad range of stunning UI components. All the components adhere to the principles of Material Design. You can use this framework for building mobile, server-side rendered, single page, and progressive web apps as well as for regular HTML pages.
To get familiar with everything Vuetify has to offer, browse the components, pick those you like the most and get hands-on experience with them in your app. Try one of the pre-made layouts, design your own theme or style your components with colors, spacings, typography and more.
Another aspect I’d like to highlight is its rich ecosystem which includes a theme generator, vuetify-loader, Cognito module, and other tools. Moreover, the components are well-documented and accompanied with nice examples.
To my mind, this framework can meet the needs of any project. Plus, you can select only specific components to be used within your app. This approach allows you to control the size of your app by making it more lightweight.
VuePress
VuePress is a static site generator tool. It offers blogging features and a plugin system. You can build custom themes and use ready-to-use community themes.
Let me break down the essence of its work. After you write the site’s content using Markdown syntax, VuePress transforms it into static HTML files. As soon as these files are loaded, your site runs as a single page application (SPA) backed by Vue, Vue Router and Webpack.
The main advantage of this approach is that you can include Vue code or components within Markdown files. That’s why the development comes out as flexible and you can create a website like a regular Vue app.
VueX
VueX is a state management system for Vue apps. You can use it as a centralized store for the application’s components and define rules that ensure that states are mutated merely in a predictable manner.
Let’s take a closer look at the structural components of VueX:
- state – an object that contains the app’s state
- getters – objects that provide methods used to access the state. They act like computed properties for stores.
- mutations – objects that provide methods for affecting the state. Mutations may remind you of events since a mutation has a string type and a handler – a function in which we modify an actual state.
- actions – objects that provide methods for triggering mutations and running async operations.
Also, it’s worth to mention modules as an inevitable part of VueX. Modules may come in handy when your application starts to scale. It’s a good practice to organize your code in modules to separate the store into individual pieces and hence simplify its maintenance. Each module has its own state, mutations, actions, and getters.
Other cool built-in features you may like are hot-reloading mutations, modules, actions, and getters during development.
To my mind, VueX perfectly copes with shared state management. But if your application is as simple as single page application, then you most likely don’t need Vuex. You should use it if you are building a medium- or large-scale single page application and facing the problem of handling the state outside of your Vue components.
Nuxt
Nuxt is another progressive Vue-based framework for building modern web applications. Under the hood of Nuxt, there are Vue official libraries (vue, vue-router, and vuex), and web dev tools (as webpack, PostCSS, and Babel) being used.
With Nuxt, you can build all kinds of Vue applications – from static landing pages to sophisticated enterprise-ready ones. It has a modular ecosystem that enables you to easily connect REST and GraphQL endpoints.
Other built-in features include server-side rendering, automatic code-splitting, ES2015+ transpilation, powerful routing system with async data and a lot more.
To my mind, the best thing about Nuxt is that it lets you enhance the development experience by providing the functionality for making the app structured and optimized.
To get a better idea of how Nuxt.js can be used, dive into examples and explore its API.
If you want to contribute to its development, you are welcome to do it on its GitHub.
Gridsome
Gridsome is a modern framework for building fast and secure websites that can be deployed to any static web host or CDN (Netflify, Amazon S3, etc). Though it’s relatively new (released in 2018), there are already a lot of adopters and followers among Vue developers. Its creators were inspired by Gatsby.js (a site generator for React). This inspiration resulted in building a similar framework but for Vue.js.
Let me explain how it works. Gridsome generates SEO-friendly HTML files based on the data source you provide within your app. The data source can be any – Markdown, CSV, Yaml, JSON, WordPress, Drupal (any other CMS), MongoDB, Airtable, etc. After loading the content, it’s turned into a single GraphQL Data Layer that serves for centralized data management. Now you can use extract this data and use it for building and deploying your Vue application.
The use of a universal GraphQL layer for all the data sources connected to the app is what makes Gridsome so unique. Due to it, data management is greatly simplified since the GraphQL layer acts as centralized storage and can be used by any page or component.
Another aspect I’d like to mention is a plugin ecosystem of Gridsome. You can take advantage of diverse plugins developed by the community of developers or even create your custom one.
Other out-of-the-box features are automatic code-splitting, static file generation, dynamic and file-based routing, hot-reloading, etc. I recommend taking the time exploring all other features of the framework.
Besides, not only it’s free but also open-source. Any contribution to the project is more than welcome since it’s a young project created and maintained by two Vue enthusiasts.
Learn more
If you are searching for ways to improve your VueJS coding skills and deepen knowledge in its specific concepts, we recommend you to explore GitConnected – there you can find plenty of tutorials on how to build apps with VueJS.